
Replace jmutai with the desired username and 1440x900 with the resolution you want to set. Where : 1 is the $DISPLAY environment variable. To control vncserver with systemd, first, create systemd unit file for the user, $ desktop service (VNC)ĮxecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'ĮxecStart=/usr/bin/vncserver %i -geometry 1440x900 -alwaysshared -fg Starting and stopping vncserver via systemd The common options are: $ cat ~/.vnc/config Supported server options can be added by editing the file ~/.vnc/config. Replace : 1 with relevance instance number given when you started it. To stop vncserver, use the command: $ vncserver -kill :1 The file should be executable: $ chmod +x ~/.vnc/xstartup Stopping vncserver As an example, to start i3wm, you'll modify the file to: $ cat ~/.vnc/xstartup xinitrc and it's sourced by vncserver when being started. At a minimum, users should start a DE from this file. There is no limit on the number of VNC servers that can be started on Linux, memory is the only limiting factor. In this case, :1 is actually TCP port 5901 (5900+1). If another instance of vncserver is started, it will run on the next highest that's free, i.e 5902 (5900+2) which shall end in : 2 as above. The :1 signifies TCP port number on which the virtual vncserver is running. If you would like to set a view-only password, please press y on the next prompt.Īs seen from the output, generated configuration will be stored under ~/.vnc/config and startup script is generated and stored in ~/.vnc/xstartup. All logs from vncserver will be stored in the file ~/.vnc/hostname:1.log.
TIGERVNC DEBIAN PASSWORD
This will prompt you to enter the password used to access your desktops, enter and verify. Starting applications specified in /home/jmutai/.vnc/xstartup New ':1 (jmutai)' desktop is :1Ĭreating default startup script /home/jmutai/.vnc/xstartupĬreating default config /home/jmutai/.vnc/config Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? n You will require a password to access your desktops. This is achieved by running the command: $ vncserver When you run vncserver for the first time, it will initialize vncserver environment, generate vncserver configuration, and add passwords for user authentication.

This connects to the VNC server allowing you to interact with a remote desktop being displayed by the VNC server. X0vncserver - This is a demonstration of a simple VNC server, it polls any X display continuously so that VNC can control it TigerVNC Client sideĪny version of TigerVNC applications comes with a cross-platform TigerVNC Viewer. Vncconfig - Used to interact with a running instance of Xvnc

Vncpasswd - When VNC authentication is enabled, vncpasswd is responsible for VNC server password management. Vncserver - This is a wrapper script used for managing starting of Xvnc daemon Xvnc - This is the VNC and X Server for TigerVNC. Since TigerVNC is a client-server application, let's look at client and server applications that are installed on your Operating system when you setup TigerVNC. In this guide, we'll look at Installing and configuration of tigervnc on Arch Linux 2018.01.01. On the site of security, TigerVNC has support for TLS encryption and other advanced authentication methods. TigerVNC is an implementation of Virtual Network Computing (VNC), which utilizes a client/server model.The level of performance provided by TigerVNC is capable of running 3D applications and playing video games.
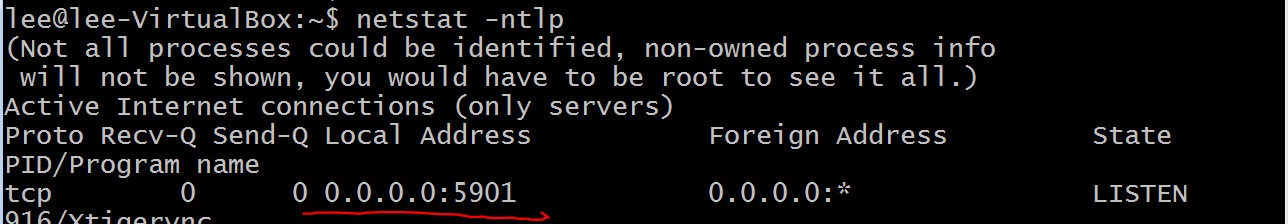
TigerVNC is an application that allows users to be able to interact with graphical applications on remote machines.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
